27 mainītis faili ar 747 papildinājumiem un 0 dzēšanām
Dalītais skats
Salīdzināšanas iespējas
-
BinārsWork 3/report/Work3_report.pdf
-
+93 -0Work 3/report/Work3_report.tex
-
+19 -0Work 3/scripts/BelongsTo.m
-
+33 -0Work 3/scripts/GivenEnv.asv
-
+36 -0Work 3/scripts/GivenEnv.m
-
+18 -0Work 3/scripts/ProjectionPoint.m
-
+14 -0Work 3/scripts/Script_0_Plots.m
-
+29 -0Work 3/scripts/Script_1_SteepDesc.m
-
+32 -0Work 3/scripts/Script_2_SteepDesc_Proj.m
-
+27 -0Work 3/scripts/Script_3_SteepDesc_Proj.m
-
+27 -0Work 3/scripts/Script_4_SteepDesc_Proj.m
-
BinārsWork 3/scripts/figures/Plot_Contour.png
-
BinārsWork 3/scripts/figures/Plot_Function.png
-
BinārsWork 3/scripts/figures/StDes_fixed_1.png
-
BinārsWork 3/scripts/figures/StDes_fixed_2.png
-
+49 -0Work 3/scripts/fmin_bisection.m
-
+32 -0Work 3/scripts/gamma_armijo.m
-
+12 -0Work 3/scripts/gamma_fixed.m
-
+24 -0Work 3/scripts/gamma_minimized.m
-
+39 -0Work 3/scripts/method_SteepDesc.m
-
+50 -0Work 3/scripts/method_SteepDesc_Proj.m
-
+42 -0Work 3/scripts/plot3dFun.m
-
+41 -0Work 3/scripts/plotContour.m
-
+54 -0Work 3/scripts/plotConvCompare.m
-
+28 -0Work 3/scripts/plotItersOverGamma.m
-
+48 -0Work 3/scripts/plotPointsOverContour.m
-
BinārsWork 3/Εργασία3.pdf
Binārs
Work 3/report/Work3_report.pdf
Parādīt failu
+ 93
- 0
Work 3/report/Work3_report.tex
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,93 @@ | |||
| % | |||
| % Optimization Techniques Work 3 report | |||
| % | |||
| % authors: | |||
| % Χρήστος Χουτουρίδης ΑΕΜ 8997 | |||
| % cchoutou@ece.auth.gr | |||
| \documentclass[a4paper, 11pt]{AUTHReport} | |||
| % Document configuration | |||
| \AuthorName{Χρήστος Χουτουρίδης} | |||
| \AuthorAEM{8997} | |||
| \AuthorMail{cchoutou@ece.auth.gr} | |||
| %\CoAuthorName{CoAuthor Name} | |||
| %\CoAuthorAEM{AEM} | |||
| %\CoAuthorMail{CoAuthor Mail} | |||
| % \WorkGroup{Ομάδα Χ} | |||
| \DocTitle{3η Εργαστηριακή Άσκηση} | |||
| \DocSubTitle{Μέθοδος Μέγιστης Καθόδου με Προβολή} | |||
| \Department{Τμήμα ΗΜΜΥ. Τομέας Ηλεκτρονικής} | |||
| \ClassName{Τεχνικές Βελτιστοποίησης} | |||
| \InstructorName{Γ. Ροβιθάκης} | |||
| \InstructorMail{rovithak@auth.gr} | |||
| \CoInstructorName{Θ. Αφορόζη} | |||
| \CoInstructorMail{taforozi@ece.auth.gr} | |||
| \CurrentDate{\today} | |||
| \usepackage{enumitem} | |||
| \usepackage{tabularx} | |||
| \usepackage{array} | |||
| \usepackage{amssymb} | |||
| \usepackage{amsfonts} | |||
| \usepackage{amsmath} | |||
| \usepackage{commath} | |||
| \usepackage{float} | |||
| \begin{document} | |||
| \InsertTitle | |||
| %\tableofcontents | |||
| \sloppy | |||
| \section{Εισαγωγή} | |||
| Η παρούσα εργασία αφορά το πρόβλημα της ελαχιστοποίησης μιας δοσμένης συνάρτησης πολλών μεταβλητών $f: \mathbb{R}^n \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ χωρίς περιορισμούς. | |||
| Για το σκοπό αυτό κάνουμε χρήση τριών μεθόδων. | |||
| Της μεθόδου μέγιστης καθόδου (Steepest Descent), της μεθόδου Newton, και της Levenberg-Marquardt. | |||
| Ακόμα για κάθε μία από αυτές θα υλοποιήσουμε τρεις διαφορετικές τεχνικές υπολογισμού βήματος. | |||
| \section{Παραδοτέα} | |||
| Τα παραδοτέα της εργασίας αποτελούνται από: | |||
| \begin{itemize} | |||
| \item Την παρούσα αναφορά. | |||
| \item Τον κατάλογο \textbf{scripts/}, που περιέχει τον κώδικα της MATLAB. | |||
| \item Το \href{https://git.hoo2.net/hoo2/OptimizationTechniques/src/branch/master/Work%203}{σύνδεσμο} με το αποθετήριο που περιέχει όλο το project με τον κώδικα της MATLAB, της αναφοράς και τα παραδοτέα. | |||
| \end{itemize} | |||
| \section{Προγραμματιστική προσέγγιση} | |||
| Για τον προγραμματισμό και εκτέλεση των μεθόδων της παρούσας εργασίας έγινε χρήση της MATLAB. | |||
| Στον κατάλογο \textbf{scripts}, περιέχονται όλες οι μέθοδοι και οι τεχνικές υπολογισμού βημάτων με τη μορφή συναρτήσεων καθώς και scripts που τις καλούν. | |||
| Για κάθε μία μέθοδο (ένα θέμα της εργασίας), υπάρχει το αντίστοιχο script που περιέχει τους υπολογισμούς, τις κλήσεις των μεθόδων και τη δημιουργία των διαγραμμάτων. | |||
| Για το πρώτο θέμα το αρχείο Script\_1\_Plots.m για το δεύτερο το Script\_2\_Steepest\_descent.m και ούτω καθεξής. | |||
| Στην παρούσα εργασία η υλοποίηση του κώδικα ακολουθεί την τεχνική της προηγούμενης εργασίας και “ομαδοποιεί” αρκετές λειτουργίες. | |||
| Πιο συγκεκριμένα. | |||
| \subsection{Symbolic expression functions} | |||
| Μία ακόμη προγραμματιστική τεχνική που ακολουθήθηκε είναι η χρήση \textbf{symbolic expression} για την αναπαράσταση των διαφορετικών αντικειμενικών συναρτήσεων. | |||
| Ο λόγος που επιλέχθηκε είναι η \textbf{δυνατότητα εξαγωγής ενός symbolic expression που αναπαριστά την κλίση $\nabla f$ και τον Εσσιανό $\nabla^2f$ μιας συνάρτησης} από την MATLAB, κάνοντας χρήση των εντολών \textit{gradient()} και \textit{hessian()}. | |||
| Αν αντίθετα χρησιμοποιούσαμε απλές συναρτήσεις, πολυώνυμα ή lambdas για την αναπαράσταση των αντικειμενικών συναρτήσεων, τότε για τον υπολογισμό της κλίσης και του Εσσιανού θα έπρεπε: | |||
| \begin{itemize} | |||
| \item Είτε να υπολογίζαμε αριθμητικά τις παραγώγους gradient και hessian μέσα στις μεθόδους, κάτι που θα εισήγαγε \textit{\textbf{αχρείαστο αριθμητικό σφάλμα}}. | |||
| \item Είτε να κάναμε χρήση δύο επιπλέων συναρτήσεων (ή πολυωνύμων) για την αναπαράσταση τους, κάτι που ουσιαστικά θα δημιουργούσε \textit{\textbf{πλεονασμό πληροφορίας εισόδου}} και άρα μεγαλύτερη πιθανότητα να κάνουμε λάθος. | |||
| \end{itemize} | |||
| Η αναπαράσταση όμως με χρήση symbolic expression είναι πιο “βαριά” όταν χρειάζεται να υπολογίσουμε την τιμή μιας συνάρτησης σε κάποιο σημείο (subs(expr, number)). | |||
| Αυτό είναι κάτι που χρειάζεται εκτενώς στον κώδικά μας. | |||
| Για το λόγο αυτό, ενώ η συνάρτηση δίνεται ως symbolic expression, μέσω αυτής υπολογίζονται αυτόματα η κλίση, ο Εσσιανός αλλά και οι “κανονικές” συναρτήσεις MATLAB που τις υλοποιούν. | |||
| Έτσι έχουμε την ακριβή αναπαράσταση της κλίσης και του Εσσιανού ως συναρτήσεις χωρίς να πληρώνουμε το κόστος της subs(). | |||
| \end{document} | |||
+ 19
- 0
Work 3/scripts/BelongsTo.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ | |||
| function [flag] = BelongsTo(x, SetLimmits) | |||
| %Checks if the x vector belongs to Set | |||
| % | |||
| % x: A vector to project | |||
| % SetLimmits: The set to project. Each line/dimension off the set has to contain the limits | |||
| % of the set to that particular dimension | |||
| % flag: True if belongs | |||
| % | |||
| flag = true; % Have faith | |||
| for i = 1:size(SetLimmits, 2) | |||
| if x(i) < SetLimmits(i,1) | |||
| flag = false; | |||
| elseif x(i) > SetLimmits(i,2) | |||
| flag = false; | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 33
- 0
Work 3/scripts/GivenEnv.asv
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,33 @@ | |||
| % Given environment | |||
| clear; | |||
| % Setup the function under test | |||
| syms x [2 1] real; | |||
| fexpr = (1/3)*x(1)^2 +3*x(2)^2; | |||
| title_fun = "$f(x) = frac{1}{3}{x_1}^2 + 3{x_2}^2$"; | |||
| % Calculate the gradient and Hessian | |||
| grad_fexpr = gradient(fexpr, x); % Gradient of f | |||
| hessian_fexpr = hessian(fexpr, x); % Hessian of f | |||
| % Convert symbolic expressions to MATLAB functions | |||
| fun = matlabFunction(fexpr, 'Vars', {x}); % Function | |||
| grad_fun = matlabFunction(grad_fexpr, 'Vars', {x}); % Gradient | |||
| hessian_fun = matlabFunction(hessian_fexpr, 'Vars', {x}); % Hessian | |||
| % Minimum reference | |||
| %Freference = @(x) x(1).^5 .* exp(-x(1).^2 - x(2).^2); | |||
| %[Xmin, Fmin] = fminsearch(Freference, [-1, -1]); | |||
| % Amijo globals | |||
| global amijo_beta; % Step reduction factor in [0.1, 0.5] (typical range: [0.1, 0.8]) | |||
| global amijo_sigma; % Sufficient decrease constant in [1e-5, 0.1] (typical range: [0.01, 0.3]) | |||
| %fixed step size globals | |||
| global gamma_fixed_step | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| image_width = 960; | |||
| image_height = 640; | |||
+ 36
- 0
Work 3/scripts/GivenEnv.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ | |||
| % Given environment | |||
| clear; | |||
| % Setup the function under test | |||
| syms x [2 1] real; | |||
| fexpr = (1/3)*x(1)^2 +3*x(2)^2; | |||
| title_fun = "$f(x) = \frac{1}{3}{x_1}^2 + 3{x_2}^2$"; | |||
| XSetLimmits = [-10, 5 ; -8, 12]; | |||
| % Calculate the gradient and Hessian | |||
| grad_fexpr = gradient(fexpr, x); % Gradient of f | |||
| hessian_fexpr = hessian(fexpr, x); % Hessian of f | |||
| % Convert symbolic expressions to MATLAB functions | |||
| fun = matlabFunction(fexpr, 'Vars', {x}); % Function | |||
| grad_fun = matlabFunction(grad_fexpr, 'Vars', {x}); % Gradient | |||
| hessian_fun = matlabFunction(hessian_fexpr, 'Vars', {x}); % Hessian | |||
| % Minimum reference | |||
| [Xmin, Fmin] = fminsearch(fun, [-1, -1]'); | |||
| Xmin = round(Xmin, 3); | |||
| Fmin = round(Fmin, 3); | |||
| % Amijo globals | |||
| global amijo_beta; % Step reduction factor in [0.1, 0.5] (typical range: [0.1, 0.8]) | |||
| global amijo_sigma; % Sufficient decrease constant in [1e-5, 0.1] (typical range: [0.01, 0.3]) | |||
| %fixed step size globals | |||
| global gamma_fixed_step | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| image_width = 960; | |||
| image_height = 640; | |||
+ 18
- 0
Work 3/scripts/ProjectionPoint.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ | |||
| function [x_p] = ProjectionPoint(x, SetLimmits) | |||
| %Project the x vector to Set, returns a point of Set close(st) to x | |||
| % | |||
| % x: A vector to project | |||
| % SetLimmits: The set to project. Each line/dimension off the set has to contain the limits | |||
| % of the set to that particular dimension | |||
| %x_p: The projected point | |||
| % | |||
| x_p = x; | |||
| for i = 1:size(SetLimmits, 2) | |||
| if x(i) < SetLimmits(i,1) | |||
| x_p(i) = SetLimmits(i,1); | |||
| elseif x(i) > SetLimmits(i,2) | |||
| x_p(i) = SetLimmits(i,2); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 14
- 0
Work 3/scripts/Script_0_Plots.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ | |||
| % Define environment (functions, gradients etc...) | |||
| GivenEnv | |||
| % | |||
| % We plot the function in the domain of x,y in [-3, 3]. | |||
| % We also plot the contour in order to get a sense of the min and maximum | |||
| % points in the x-y plane | |||
| % | |||
| % 3d plot the function | |||
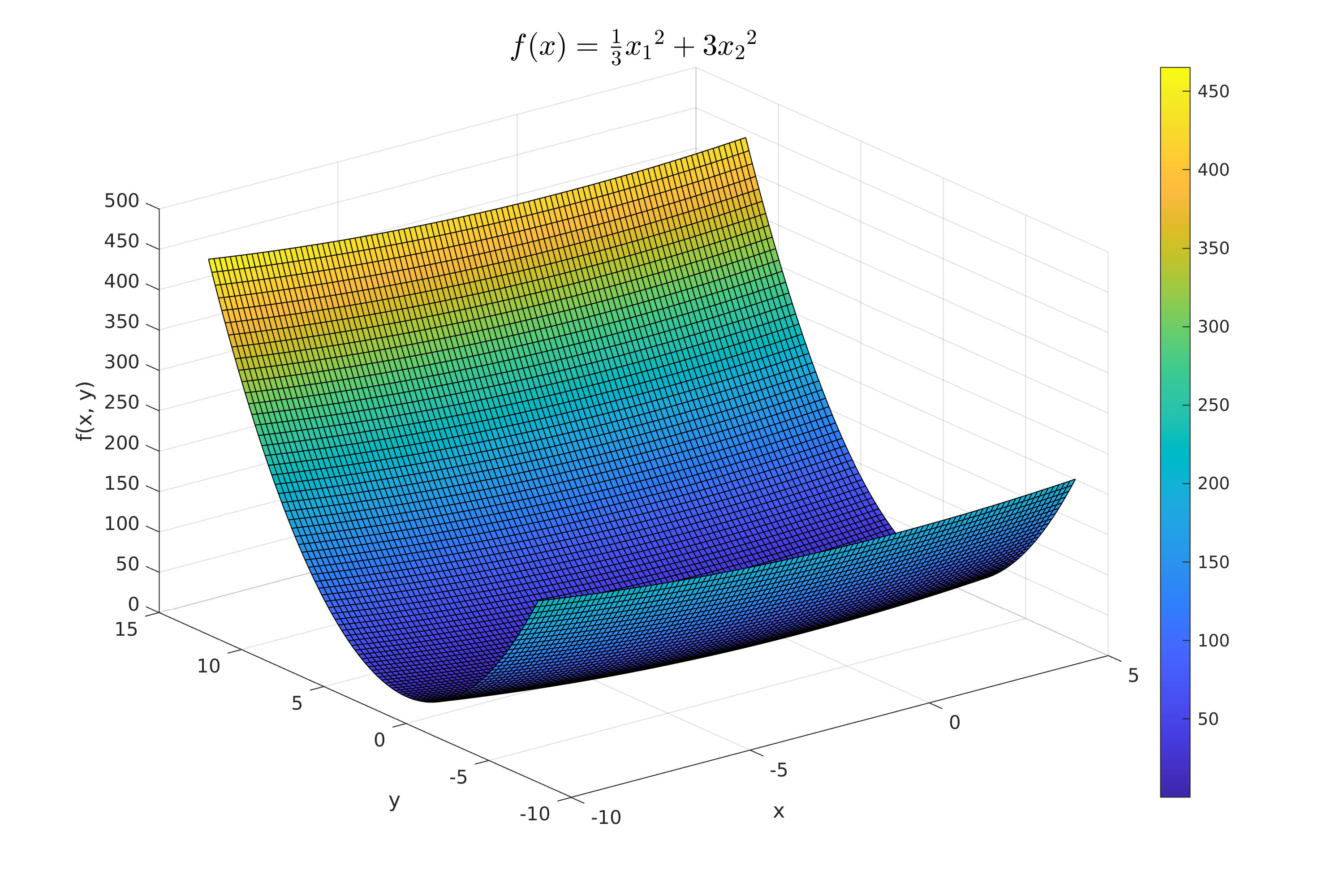
| plot3dFun(fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, title_fun, "figures/Plot_Function.png"); | |||
| % Plot isobaric lines | |||
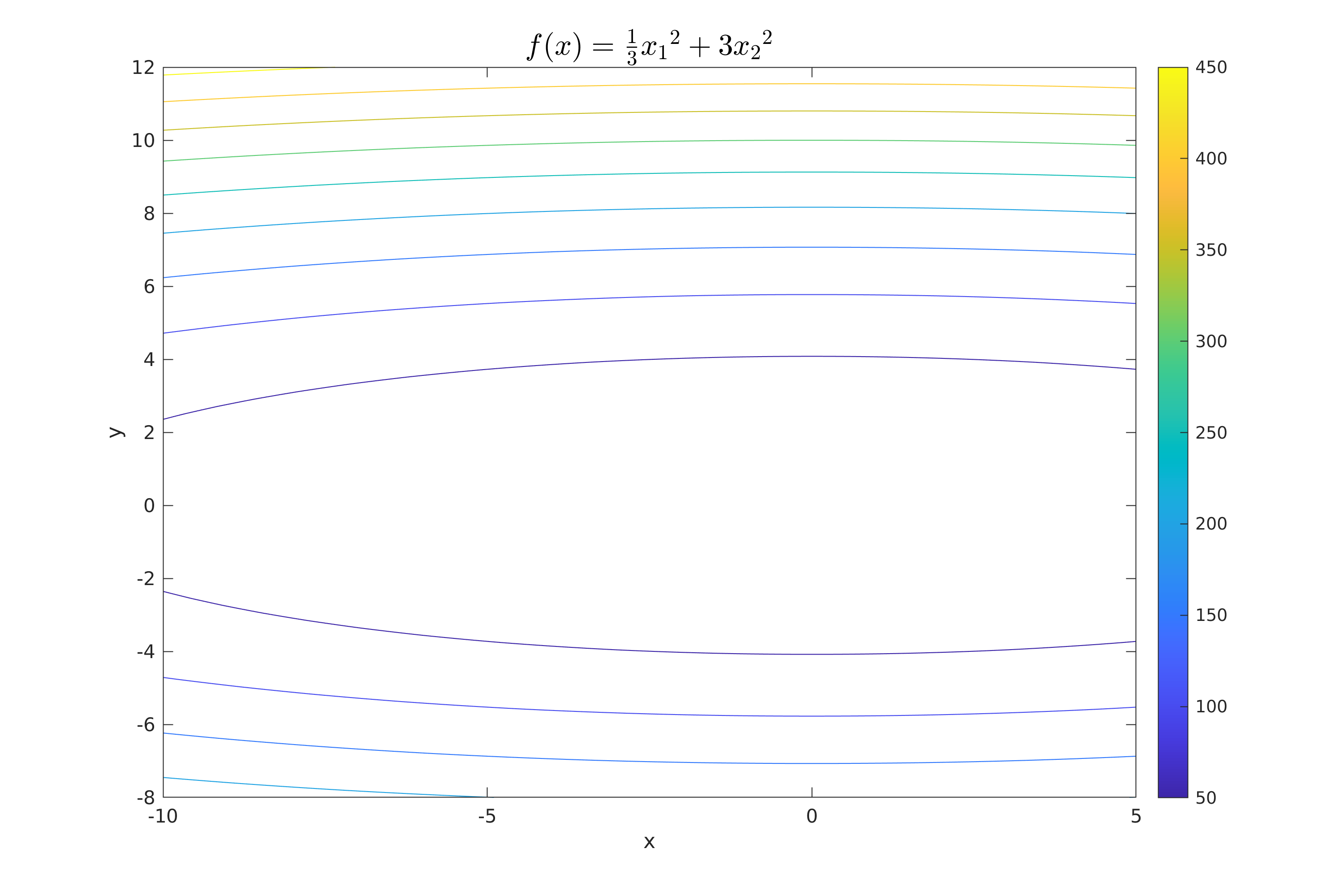
| plotContour(fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, title_fun, "figures/Plot_Contour.png"); | |||
+ 29
- 0
Work 3/scripts/Script_1_SteepDesc.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,29 @@ | |||
| % Define environment (functions, gradients etc...) | |||
| GivenEnv | |||
| % Define parameters | |||
| max_iter = 1000; % Maximum iterations | |||
| tol = 1e-4; % Tolerance | |||
| % Point x0 = (1, 1) | |||
| % ========================================================================= | |||
| point = 1; | |||
| x0 = [5, -5]'; | |||
| point_str = "[" + x0(1) + ", " + x0(2) + "]"; | |||
| f = fun(x0); | |||
| gf = grad_fun(x0); | |||
| hf = hessian_fun(x0); | |||
| fprintf('Initial point (%d, %d), f = %f, grad = [%f;%f], hessian = [%f %f ; %f %f]=> Method applicable\n', x0, f, gf, hf); | |||
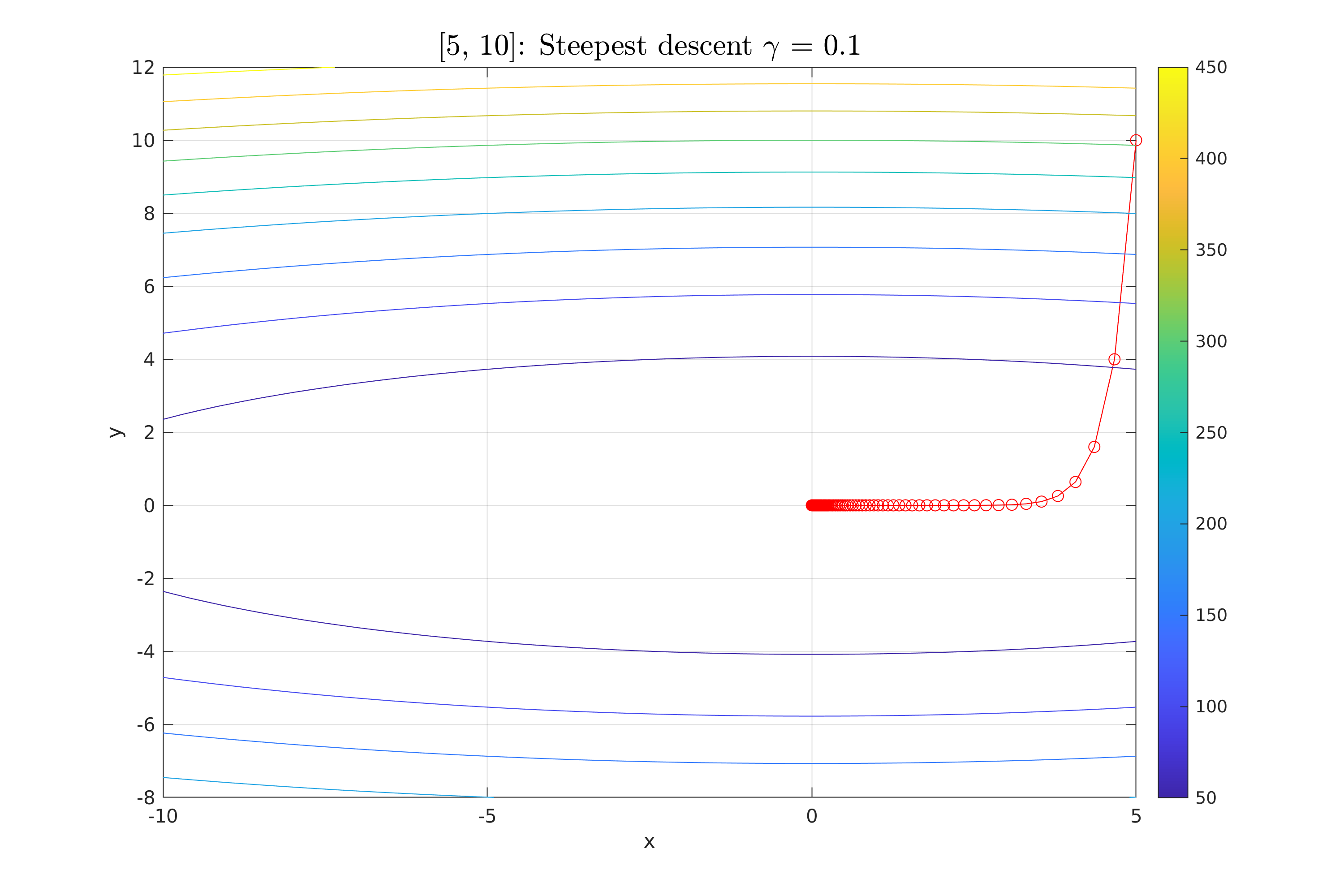
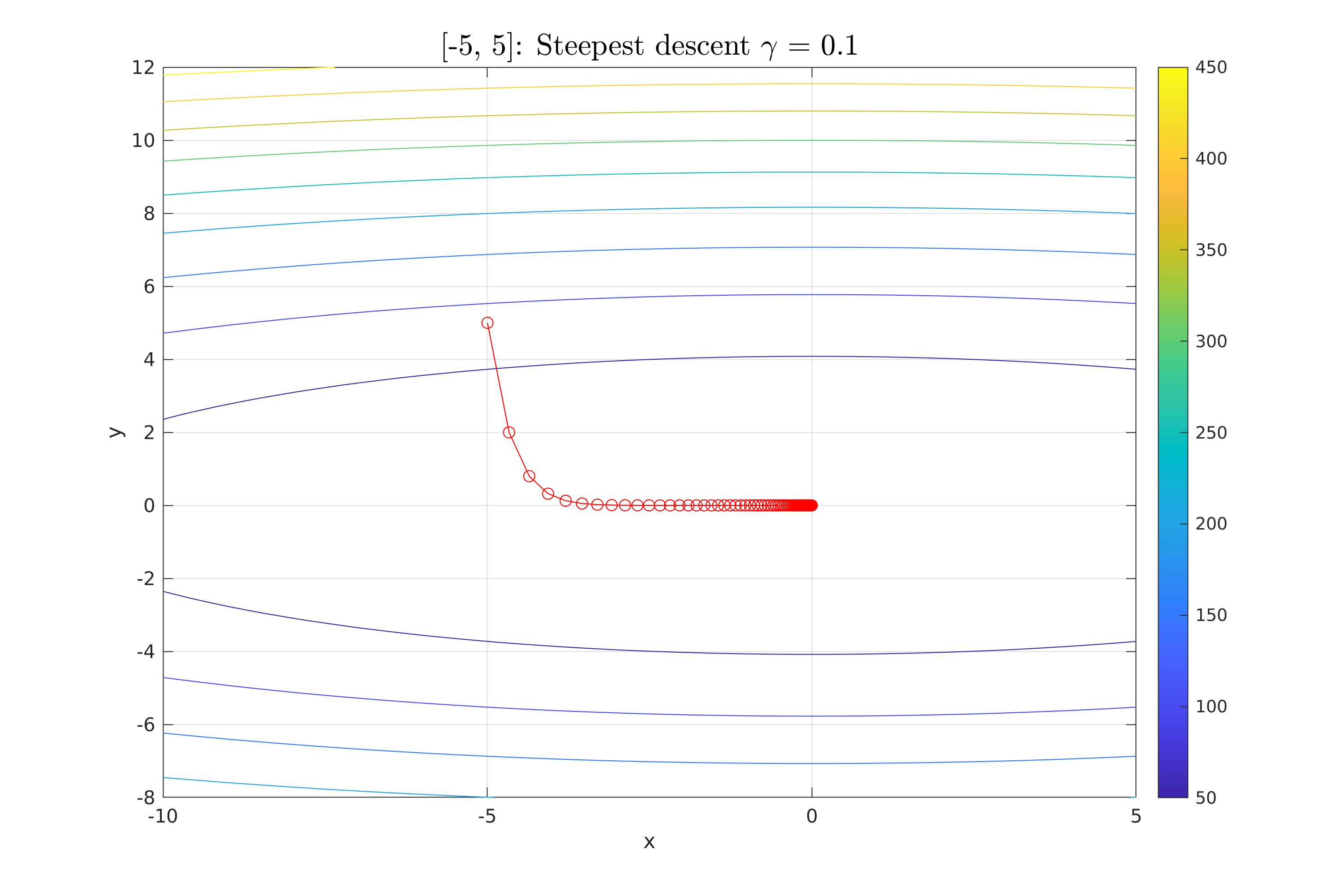
| for g=[0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 3, 5] | |||
| gamma_fixed_step = g; | |||
| [x_fixed, f_fixed, kk] = method_SteepDesc(fun, grad_fun, x0, tol, max_iter, 'fixed'); | |||
| fprintf('Fixed step g=%f: Initial point (%f, %f), steps:%d, Final (x1,x2)=(%f, %f), f(x1,x2)=%f\n', g, x0, kk, x_fixed(:, end), f_fixed(end)); | |||
| if g <= 1 | |||
| plotPointsOverContour(x_fixed, fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, point_str + ": Steepest descent $\gamma$ = " + gamma_fixed_step, ""); | |||
| else | |||
| plotPointsOverContour(x_fixed, fun, [-500, 500], [-500, 500], 100, point_str + ": Steepest descent $\gamma$ = " + gamma_fixed_step, ""); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 32
- 0
Work 3/scripts/Script_2_SteepDesc_Proj.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ | |||
| % Define environment (functions, gradients etc...) | |||
| GivenEnv | |||
| % Settings | |||
| max_iter = 1000; % Maximum iterations | |||
| % Define parameters | |||
| % ========================================================================= | |||
| x0 = [5, -5]'; | |||
| gamma = 0.5; | |||
| sk_step = 5; | |||
| tol = 0.01; % Tolerance | |||
| point_str = "[" + x0(1) + ", " + x0(2) + "]"; | |||
| f = fun(x0); | |||
| gf = grad_fun(x0); | |||
| hf = hessian_fun(x0); | |||
| fprintf('Initial point (%d, %d), f = %f, grad = [%f;%f], hessian = [%f %f ; %f %f]=> Method applicable\n', x0, f, gf, hf); | |||
| gamma_fixed_step = gamma; | |||
| [x_fixed, f_fixed, kk] = method_SteepDesc_Proj(fun, grad_fun, x0, sk_step, XSetLimmits, tol, max_iter, 'fixed'); | |||
| fprintf('Fixed step g=%f: Initial point (%f, %f), steps:%d, Final (x1,x2)=(%f, %f), f(x1,x2)=%f\n', gamma_fixed_step, x0, kk, x_fixed(:, end), f_fixed(end)); | |||
| plotPointsOverContour(x_fixed, fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, point_str + ": Steepest descent $\gamma$ = " + gamma_fixed_step, ""); | |||
| %[x_minimized, f_minimized, kk] = method_SteepDesc_Proj(fun, grad_fun, x0, sk_step, XSetLimmits, tol, max_iter, 'minimized'); | |||
| %fprintf('Minimized f: Initial point (%f, %f), steps:%d, Final (x1,x2)=(%f, %f), f(x1,x2)=%f\n', x0, kk, x_fixed(:, end), f_fixed(end)); | |||
| %plotPointsOverContour(x_fixed, fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, point_str + ": Steepest descent minimized", ""); | |||
+ 27
- 0
Work 3/scripts/Script_3_SteepDesc_Proj.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ | |||
| % Define environment (functions, gradients etc...) | |||
| GivenEnv | |||
| % Settings | |||
| max_iter = 1000; % Maximum iterations | |||
| % Define parameters | |||
| % ========================================================================= | |||
| x0 = [-5, 10]'; | |||
| gamma = 0.1; | |||
| sk_step = 55; | |||
| tol = 0.01; % Tolerance | |||
| point_str = "[" + x0(1) + ", " + x0(2) + "]"; | |||
| f = fun(x0); | |||
| gf = grad_fun(x0); | |||
| hf = hessian_fun(x0); | |||
| fprintf('Initial point (%d, %d), f = %f, grad = [%f;%f], hessian = [%f %f ; %f %f]=> Method applicable\n', x0, f, gf, hf); | |||
| gamma_fixed_step = gamma; | |||
| [x_fixed, f_fixed, kk] = method_SteepDesc_Proj(fun, grad_fun, x0, sk_step, XSetLimmits, tol, max_iter, 'fixed'); | |||
| fprintf('Fixed step g=%f: Initial point (%f, %f), steps:%d, Final (x1,x2)=(%f, %f), f(x1,x2)=%f\n', gamma_fixed_step, x0, kk, x_fixed(:, end), f_fixed(end)); | |||
| plotPointsOverContour(x_fixed, fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, point_str + ": Steepest descent $\gamma$ = " + gamma_fixed_step, ""); | |||
+ 27
- 0
Work 3/scripts/Script_4_SteepDesc_Proj.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ | |||
| % Define environment (functions, gradients etc...) | |||
| GivenEnv | |||
| % Settings | |||
| max_iter = 1000; % Maximum iterations | |||
| % Define parameters | |||
| % ========================================================================= | |||
| x0 = [8, -10]'; | |||
| gamma = 0.2; | |||
| sk_step = 0.1; | |||
| tol = 0.01; % Tolerance | |||
| point_str = "[" + x0(1) + ", " + x0(2) + "]"; | |||
| f = fun(x0); | |||
| gf = grad_fun(x0); | |||
| hf = hessian_fun(x0); | |||
| fprintf('Initial point (%d, %d), f = %f, grad = [%f;%f], hessian = [%f %f ; %f %f]=> Method applicable\n', x0, f, gf, hf); | |||
| gamma_fixed_step = gamma; | |||
| [x_fixed, f_fixed, kk] = method_SteepDesc_Proj(fun, grad_fun, x0, sk_step, XSetLimmits, tol, max_iter, 'fixed'); | |||
| fprintf('Fixed step g=%f: Initial point (%f, %f), steps:%d, Final (x1,x2)=(%f, %f), f(x1,x2)=%f\n', gamma_fixed_step, x0, kk, x_fixed(:, end), f_fixed(end)); | |||
| plotPointsOverContour(x_fixed, fun, XSetLimmits(1, :), XSetLimmits(2, :), 100, point_str + ": Steepest descent $\gamma$ = " + gamma_fixed_step, ""); | |||
Binārs
Work 3/scripts/figures/Plot_Contour.png
Parādīt failu
Binārs
Work 3/scripts/figures/Plot_Function.png
Parādīt failu
Binārs
Work 3/scripts/figures/StDes_fixed_1.png
Parādīt failu
Binārs
Work 3/scripts/figures/StDes_fixed_2.png
Parādīt failu
+ 49
- 0
Work 3/scripts/fmin_bisection.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,49 @@ | |||
| function [a, b, k, n] = fmin_bisection(fun, alpha, beta, epsilon, lambda) | |||
| % Bisection method for finding the local minimum of a function. | |||
| % | |||
| % fun: The objective function | |||
| % alpha: (number) The starting point of the interval in which we seek | |||
| % for minimum | |||
| % beta: (number) The ending point of the interval in which we seek | |||
| % for minimum | |||
| % epsilon: (number) The epsilon value (distance from midpoint) | |||
| % lambda: (number) The lambda value (accuracy) | |||
| % | |||
| % return: | |||
| % a: (vector) Starting points of the interval for each iteration | |||
| % b: (vector) Ending points of the interval for each iteration | |||
| % k: (number) The number of iterations | |||
| % n: (number) The calls of objective function fun_expr | |||
| % | |||
| % Error checking | |||
| if alpha > beta || 2*epsilon >= lambda || lambda <= 0 | |||
| error ('Input criteria not met') | |||
| end | |||
| % Init | |||
| a = alpha; | |||
| b = beta; | |||
| n = 0; | |||
| k=1; | |||
| while b(k) - a(k) > lambda | |||
| % bisect [a,b] | |||
| mid = (a(k) + b(k)) / 2; | |||
| x_1 = mid - epsilon; | |||
| x_2 = mid + epsilon; | |||
| % set new search interval | |||
| k = k + 1; | |||
| if fun(x_1) < fun(x_2) | |||
| a(k) = a(k-1); | |||
| b(k) = x_2; | |||
| else | |||
| a(k) = x_1; | |||
| b(k) = b(k-1); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 32
- 0
Work 3/scripts/gamma_armijo.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ | |||
| function [gamma] = gamma_armijo(f, grad_f, dk, xk) | |||
| % Calculates the best step based on amijo method | |||
| % | |||
| % f(xk+ γk*dk) ≤ f(xk) + σ * γk * dk^T * ∇f(xk) | |||
| % γk = β*γk_0 | |||
| % | |||
| % f: Objective function | |||
| % grad_fun: Gradient function of f | |||
| % dk: Current value of selected direction -∇f or -inv{H}*∇f or -inv{H + lI}*∇f | |||
| % xk: Current point (x,y) | |||
| % beta: beta factor in [0.1, 0.5] | |||
| % signam: sigma factor in (0, 0.1] | |||
| global amijo_beta | |||
| global amijo_sigma | |||
| gf = grad_f(xk); | |||
| gamma = 1; % Start with a step size of 1 | |||
| % Perform Armijo line search | |||
| while f(xk + gamma * dk) > f(xk) + amijo_sigma * gamma * dk * gf | |||
| %while f(xk(1) + gamma * dk(1), xk(2) + gamma * dk(2)) > ... | |||
| % f(xk(1), xk(2)) + amijo_sigma * gamma * norm(dk)^2 | |||
| gamma = amijo_beta * gamma; % Reduce step size | |||
| if gamma < 1e-12 % Safeguard to prevent infinite reduction | |||
| warning('Armijo step size became too small.'); | |||
| break; | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 12
- 0
Work 3/scripts/gamma_fixed.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,12 @@ | |||
| function [gamma] = gamma_fixed(~, ~, ~, ~) | |||
| % Return a fixed step | |||
| % | |||
| % This is for completion and code symmetry. | |||
| % | |||
| global gamma_fixed_step | |||
| % Perform line search | |||
| gamma = gamma_fixed_step; | |||
| end | |||
+ 24
- 0
Work 3/scripts/gamma_minimized.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,24 @@ | |||
| function [gamma] = gamma_minimized(f, ~, dk, xk) | |||
| % Calculates the step based on minimizing f(xk− γk*dk) | |||
| % | |||
| % | |||
| % f: Objective function | |||
| % ~: Gradient function of f - Not used | |||
| % dk: Current value of selected direction -∇f or -inv{H}*∇f or -inv{H + lI}*∇f | |||
| % xk: Current point (x,y) | |||
| % Define the line search function fmin(g) = f(xk - g * dk) | |||
| fmin = @(g) f(xk) + g * dk; | |||
| % find g that minimizes fmin | |||
| e = 0.0001; | |||
| l = 0.001; | |||
| [a,b,k,~] = fmin_bisection(fmin, 0.0001, 1, e, l); % g in (0, 1] | |||
| gamma = 0.5*(a(k) + b(k)); | |||
| % Define the line search function fmin(g) = f(xk - g * dk) | |||
| %fmin = @(g) f(xk(1) - gamma * dk(1), xk(2) - gamma * dk(2)); | |||
| % find g that minimizes fmin | |||
| %gamma = fminbnd(g, 0, 1); | |||
| end | |||
+ 39
- 0
Work 3/scripts/method_SteepDesc.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,39 @@ | |||
| function [x_vals, f_vals, k] = method_SteepDesc(f, grad_f, xk, tol, max_iter, mode) | |||
| % f: Objective function | |||
| % grad_f: Gradient of the function | |||
| % xk: Initial point [x0; y0] | |||
| % tol: Tolerance for stopping criterion | |||
| % max_iter: Maximum number of iterations | |||
| % x_vals: Vector with the (x,y) values until minimum | |||
| % f_vals: Vector with f(x,y) values until minimum | |||
| % k: Number of iterations | |||
| if strcmp(mode, 'armijo') == 1 | |||
| gamma_f = @(f, grad_f, dk, xk) gamma_armijo(f, grad_f, dk, xk); | |||
| elseif strcmp(mode, 'minimized') == 1 | |||
| gamma_f = @(f, grad_f, dk, xk) gamma_minimized(f, grad_f, dk, xk); | |||
| else % mode == 'fixed' | |||
| gamma_f = @(f, grad_f, dk, xk) gamma_fixed(f, grad_f, dk, xk); | |||
| end | |||
| % Storage for iterations, begin with the first point | |||
| x_vals = xk; | |||
| f_vals = f(xk); | |||
| for k = 1:max_iter | |||
| % Check for convergence | |||
| if norm(grad_f(xk)) < tol | |||
| break; | |||
| end | |||
| dk = - grad_f(xk); % Steepset descent direction | |||
| gk = gamma_f(f, grad_f, dk, xk); % Calculate gamma | |||
| x_next = xk + gk * dk; % Update step | |||
| f_next = f(x_next); | |||
| xk = x_next; % Update point | |||
| x_vals = [x_vals, x_next]; % Store values | |||
| f_vals = [f_vals, f_next]; % Store function values | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 50
- 0
Work 3/scripts/method_SteepDesc_Proj.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,50 @@ | |||
| function [x_vals, f_vals, k] = method_SteepDesc_Proj(f, grad_f, xk, sk, limmits, tol, max_iter, mode) | |||
| % f: Objective function | |||
| % grad_f: Gradient of the function | |||
| % xk: Initial point [x0; y0] | |||
| % sk: Step size (fixed positive scalar) | |||
| % limits: Bounds of the feasible set for each dimension | |||
| % tol: Tolerance for stopping criterion | |||
| % max_iter: Maximum number of iterations | |||
| % x_vals: Vector with the (x,y) values until minimum | |||
| % f_vals: Vector with f(x,y) values until minimum | |||
| % k: Number of iterations | |||
| if strcmp(mode, 'armijo') == 1 | |||
| gamma_f = @(f, grad_f, dk, xk) gamma_armijo(f, grad_f, dk, xk); | |||
| elseif strcmp(mode, 'minimized') == 1 | |||
| gamma_f = @(f, grad_f, dk, xk) gamma_minimized(f, grad_f, dk, xk); | |||
| else % mode == 'fixed' | |||
| gamma_f = @(f, grad_f, dk, xk) gamma_fixed(f, grad_f, dk, xk); | |||
| end | |||
| % Project the first point if needed | |||
| xk = ProjectionPoint(xk, limmits); | |||
| % Storage for iterations, begin with the first point | |||
| x_vals = xk; | |||
| f_vals = f(xk); | |||
| for k = 1:max_iter | |||
| % Check for convergence | |||
| if norm(grad_f(xk)) < tol | |||
| break; | |||
| end | |||
| dk = - grad_f(xk); % Steepset descent direction | |||
| % First calculate xk-bar and project it if nessesary | |||
| xkbar = xk + sk * dk; | |||
| xkbar = ProjectionPoint(xkbar, limmits); | |||
| dk = (xkbar - xk); % Steepest descent projection direction | |||
| gk = gamma_f(f, grad_f, dk, xk); % Calculate gamma | |||
| x_next = xk + gk * dk; % Update step | |||
| f_next = f(x_next); | |||
| xk = x_next; % Update point | |||
| x_vals = [x_vals, x_next]; % Store values | |||
| f_vals = [f_vals, f_next]; % Store function values | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 42
- 0
Work 3/scripts/plot3dFun.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,42 @@ | |||
| function plot3dFun(fun, x_lim, y_lim, size, plot_title, filename) | |||
| % 3D plots a function | |||
| % fun: The function to plot | |||
| % x_lim: The range for x axis. ex: [-2, 2] | |||
| % y_lim: The range for y axis. ex: [0, 2] | |||
| % size: The number of points for each axis | |||
| % plot_title: The latex title for the plot | |||
| % | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| % Generate a grid for x and y | |||
| x_space = linspace(x_lim(1), x_lim(2), size); | |||
| y_space = linspace(y_lim(1), y_lim(2), size); | |||
| [X, Y] = meshgrid(x_space, y_space); | |||
| % Evaluate the function on the grid | |||
| for i = 1:size | |||
| for j = 1:size | |||
| % Pass each [x1; x2] as input to fun | |||
| Z(i, j) = fun([X(i, j); Y(i, j)]); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| % 3D plot | |||
| figure('Name', 'f(x,y)', 'NumberTitle', 'off'); | |||
| set(gcf, 'Position', [100, 100, image_width, image_height]); % Set the figure size | |||
| surf(X, Y, Z); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| xlabel('x1'); % Label for x-axis | |||
| ylabel('x2'); % Label for y-axis | |||
| zlabel('f(x, y)'); % Label for z-axis | |||
| title(plot_title, 'Interpreter', 'latex', 'FontSize', 16); % Title of the plot | |||
| colorbar; | |||
| % save the figure | |||
| if strcmp(filename, '') == 0 | |||
| print(gcf, filename, '-dpng', '-r300'); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 41
- 0
Work 3/scripts/plotContour.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,41 @@ | |||
| function plotContour(fun, x_lim, y_lim, size, plot_title, filename) | |||
| % plot the contour of a function | |||
| % fun: The function to plot | |||
| % x_lim: The range for x axis. ex: [-2, 2] | |||
| % y_lim: The range for y axis. ex: [0, 2] | |||
| % size: The number of points for each axis | |||
| % plot_title: The latex title for the plot | |||
| % | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| % Generate a grid for x and y | |||
| x_space = linspace(x_lim(1), x_lim(2), size); | |||
| y_space = linspace(y_lim(1), y_lim(2), size); | |||
| [X, Y] = meshgrid(x_space, y_space); | |||
| % Evaluate the function on the grid | |||
| for i = 1:size | |||
| for j = 1:size | |||
| % Pass each [x1; x2] as input to fun | |||
| Z(i, j) = fun([X(i, j); Y(i, j)]); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| % Contour | |||
| figure('Name', 'Contours of f(x1,x2)', 'NumberTitle', 'off'); | |||
| set(gcf, 'Position', [100, 100, image_width, image_height]); % Set the figure size | |||
| contour(X, Y, Z); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| xlabel('x1'); % Label for x-axis | |||
| ylabel('x2'); % Label for y-axis | |||
| title(plot_title, 'Interpreter', 'latex', 'FontSize', 16); % Title of the plot | |||
| colorbar; | |||
| % save the figure | |||
| if strcmp(filename, '') == 0 | |||
| print(gcf, filename, '-dpng', '-r300'); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 54
- 0
Work 3/scripts/plotConvCompare.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,54 @@ | |||
| function plotConvCompare(points_1, title_1, points_2, title_2, points_3, title_3, Min_point, plot_title, filename) | |||
| % 3D plots a function | |||
| % points: The points to plot | |||
| % contur_fun: The function for contour plot | |||
| % x_lim: The range for x axis. ex: [-2, 2] | |||
| % y_lim: The range for y axis. ex: [0, 2] | |||
| % size: The number of points for each axis | |||
| % plot_title: The latex title for the plot | |||
| % filename: The filename to save the plot (if exists) | |||
| % | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| distances_1 = sqrt((points_1(1, :) - Min_point(1)).^2 + (points_1(2, :) - Min_point(2)).^2); | |||
| distances_2 = sqrt((points_2(1, :) - Min_point(1)).^2 + (points_2(2, :) - Min_point(2)).^2); | |||
| distances_3 = sqrt((points_3(1, :) - Min_point(1)).^2 + (points_3(2, :) - Min_point(2)).^2); | |||
| % 2D plot | |||
| figure('Name', 'Convergence compare', 'NumberTitle', 'off'); | |||
| set(gcf, 'Position', [100, 100, image_width, image_height]); % Set the figure size | |||
| title(plot_title, 'Interpreter', 'latex', 'FontSize', 16); % Title of the plot | |||
| % One | |||
| subplot(3, 1, 1); | |||
| plot(distances_1, '-o'); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| ylabel(title_1, 'Interpreter', 'none'); | |||
| xlabel('Step'); | |||
| grid on | |||
| % One | |||
| subplot(3, 1, 2); | |||
| plot(distances_2, '-o'); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| ylabel(title_2, 'Interpreter', 'none'); | |||
| xlabel('Step'); | |||
| grid on | |||
| % One | |||
| subplot(3, 1, 3); | |||
| plot(distances_3, '-o'); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| ylabel(title_3, 'Interpreter', 'none'); | |||
| xlabel('Step'); | |||
| grid on | |||
| % save the figure | |||
| if strcmp(filename, '') == 0 | |||
| print(gcf, filename, '-dpng', '-r300'); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 28
- 0
Work 3/scripts/plotItersOverGamma.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | |||
| function plotItersOverGamma(gamma, iterations, plot_title, filename) | |||
| % 3D plots a function | |||
| % fun: The points to plot | |||
| % contur_fun: The function for contour plot | |||
| % x_lim: The range for x axis. ex: [-2, 2] | |||
| % y_lim: The range for y axis. ex: [0, 2] | |||
| % size: The number of points for each axis | |||
| % plot_title: The latex title for the plot | |||
| % filename: The filename to save the plot (if exists) | |||
| % | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| figure('Name', 'Iterations_over_gamma', 'NumberTitle', 'off'); | |||
| set(gcf, 'Position', [100, 100, image_width, image_height]); % Set the figure size | |||
| plot(gamma, iterations, '*r', 'LineWidth', 2); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| title(plot_title, 'Interpreter', 'latex', 'FontSize', 16); % Title of the plot | |||
| xlabel('\gamma') ; | |||
| ylabel('Iterations'); | |||
| % save the figure | |||
| if strcmp(filename, '') == 0 | |||
| print(gcf, filename, '-dpng', '-r300'); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
+ 48
- 0
Work 3/scripts/plotPointsOverContour.m
Parādīt failu
| @@ -0,0 +1,48 @@ | |||
| function plotPointsOverContour(points, contour_fun, x_lim, y_lim, size, plot_title, filename) | |||
| % 3D plots a function | |||
| % points: The points to plot | |||
| % contur_fun: The function for contour plot | |||
| % x_lim: The range for x axis. ex: [-2, 2] | |||
| % y_lim: The range for y axis. ex: [0, 2] | |||
| % size: The number of points for each axis | |||
| % plot_title: The latex title for the plot | |||
| % filename: The filename to save the plot (if exists) | |||
| % | |||
| global image_width, | |||
| global image_height; | |||
| % Generate a grid for x and y | |||
| x_space = linspace(x_lim(1), x_lim(2), size); | |||
| y_space = linspace(y_lim(1), y_lim(2), size); | |||
| [X, Y] = meshgrid(x_space, y_space); | |||
| % Evaluate the function on the grid | |||
| for i = 1:size | |||
| for j = 1:size | |||
| % Pass each [x1; x2] as input to fun | |||
| Z(i, j) = contour_fun([X(i, j); Y(i, j)]); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||
| % 2D plot | |||
| figure('Name', '(x1,x2) convergence', 'NumberTitle', 'off'); | |||
| set(gcf, 'Position', [100, 100, image_width, image_height]); % Set the figure size | |||
| plot(points(1, :), points(2, :), '-or'); | |||
| hold on | |||
| contour(X, Y, Z); | |||
| % Customize the plot | |||
| xlim(x_lim); | |||
| ylim(y_lim); | |||
| xlabel('x1'); % Label for x-axis | |||
| ylabel('x2'); % Label for y-axis | |||
| grid on | |||
| title(plot_title, 'Interpreter', 'latex', 'FontSize', 16); % Title of the plot | |||
| colorbar; | |||
| % save the figure | |||
| if strcmp(filename, '') == 0 | |||
| print(gcf, filename, '-dpng', '-r300'); | |||
| end | |||
| end | |||